Cpp_流式IO处理_字符控制_pf操作符
内容
Cpp的基于流的IO系统
- ostream中
<<运算符方法中的参数:pf控制符
<<
<<叫做流插入运算符(insertion operator)。把后面跟随的内容插入到流中。
1 | int main() |
<<后面支持跟着哪些东西
- 数字类型(arithmetic types)
- 流缓冲(stream buffers)
- 控制符(manipulators)
>>
>>称作流析出运算符(extraction operator)。
控制符号
std::endl
end of line
std::endl是定义在ostream中的函数。
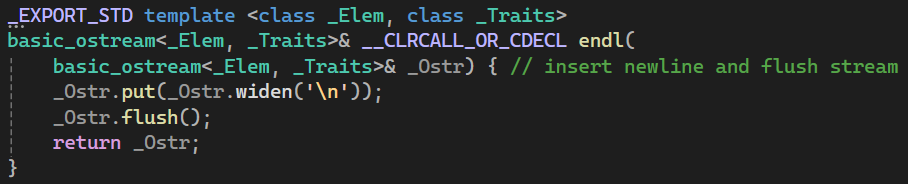
实际上就是输出了一个\n,并且刷新缓冲区。
cout哪来的?ostream
在<iostream>中,cout是这么定义的:
1 | extern ostream cout; |
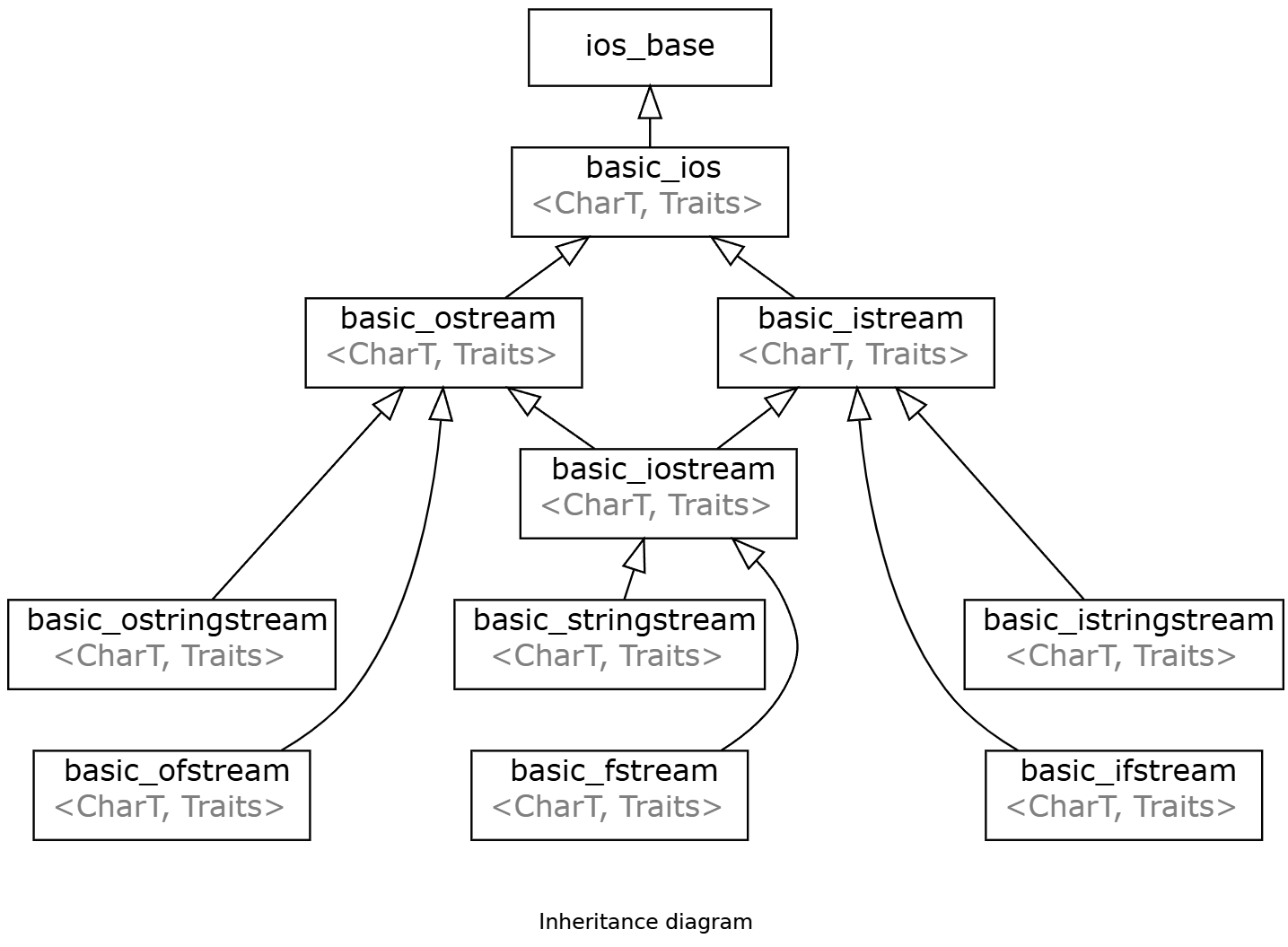
iostream是继承于ostream、iostream的。
在<ostream>中,ostream是basic_ostream<char>的别名。
1 | typedef basic_ostream<char> ostream; |
cout、cerr、clog是定义于basic_ostream<char>,即ostream的对象。
关于详细的:ostream
ostream的方法
width方法控制数字宽度
cout本身有一些方法,比如width就是。通过std::cout.width(n)进行调用。
这个变量是继承于std::ios_base得来的。std::ios_base::width - cppreference.com
1 | int main() |
输出:
1 | 12345678 |
可以看到,width为10时,如果不足10个字符,则前面空出补位。
precision方法控制浮点数的精度
precision
和width一样,是cout的方法。
1 |
|
output:
1 | 3.1416 |
基于流插入的形式进行的字符控制
ostream中的pf
https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/ostream/ostream/operator<</
pf是<<方法中值得注意的参数。pf是一个函数指针。可以填入不同的操作符(manipulator)。
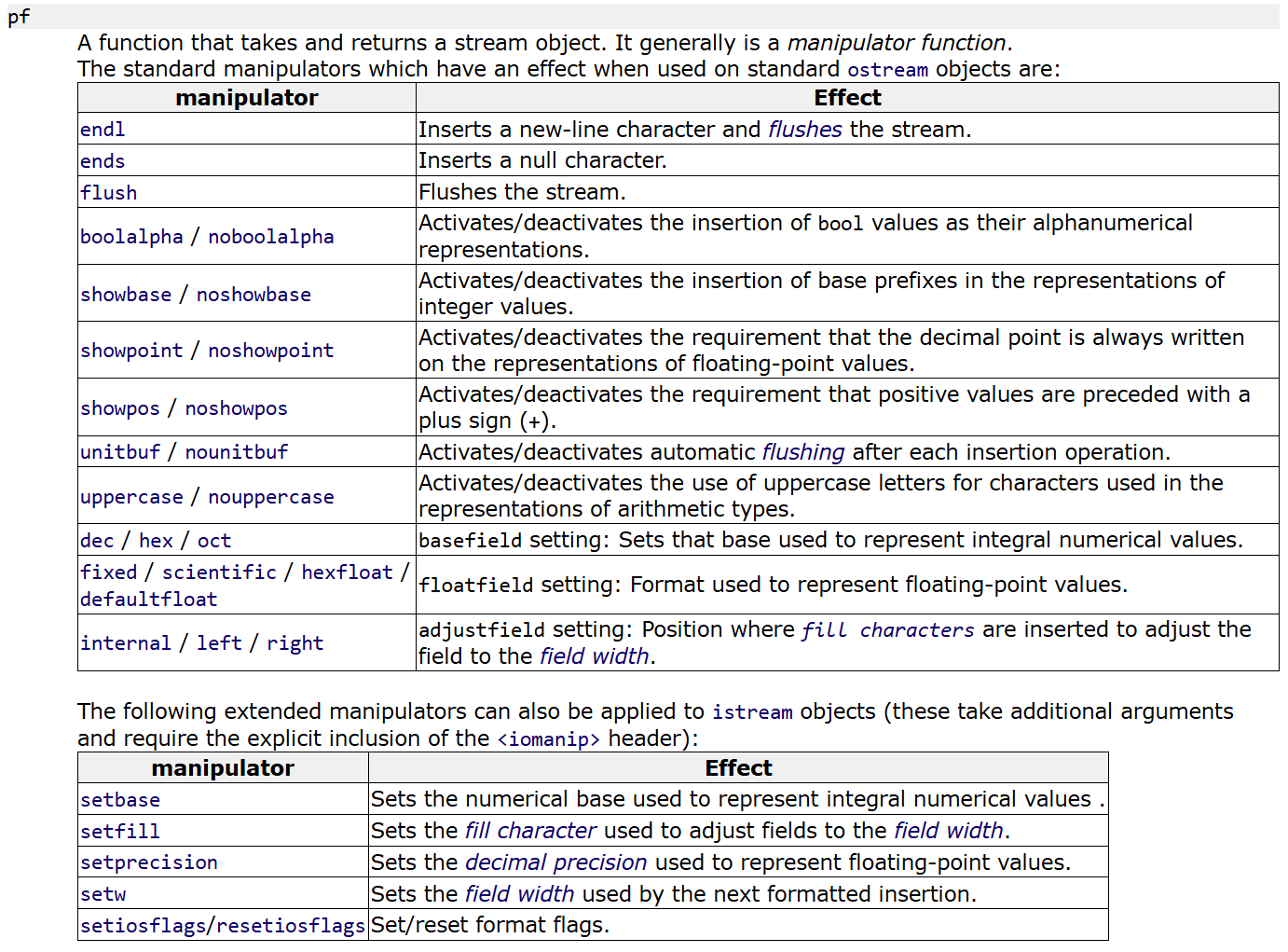
操作符(manipulator)
endl
其实我们最常见的std::endl就是一个。
1 | // Defined in header <ostream> |
可以看到,endl实际上是一个函数。作用是往cout写入一个\n,然后flush一下cout,最后再返回cout。
boolalpha控制bool输出形式
除了endl这个manipulator,还有其他更专用的。如boolalpha / noboolalpha。(定义于标准库标头<ios>)
默认下的bool类型:false输出0,true输出1。插入boolalpha后,就会false输出false、true输出true。而且一旦插入了boolalpha,就会持续保持状态,因为cout是一个全局对象。如果要恢复原态需要再次插入noboolalpha。
1 | int main() |
setw
在<iomanip>定义的std::setw也可以控制width:
std::setw - cppreference.com
setw是一个扩展的manipulator。需要另外引入
<iomanip>
它也可以控制宽度,但较于width,它是基于流插入的形式进行的。通过std::setw(n)进行。
1 |
|
output:
1 | -77 |
left、right、internal
可以配合internal、left、right进行对齐。(from <ios>)
std::left, std::right, std::internal - cppreference.com
- internal是符号左、数字右;
- left是符号和数字整体左;
- right是符号和数字整体右。
示例
经过测试,必须每次都事先设置width,才能有效果。
1 | int main() |
output:
1 | - 77 |
setprecision
std::setprecision - cppreference.com
setprecision也是一个扩展的manipulator。(from <iomanip>)
和precision方法一样,可以用于控制数字的精度,但setprecision是基于插入形式的。
1 |
|
output:
1 | 3.1416 |
控制数字类型的输出
还有showbase、showpoint、showpos、uppercase、dec / hex / oct等等(from <ios>)
dec / hex / oct的作用在于控制输出数字类型的进制。比如
1 | int main() |
showbase的作用在于输出时不同进制数加前缀,比如开启了showbase后,输出16进制数:
1 | int main() |
uppercase的作用是输出数字类型时,区分大小写格式。比如开启uppercase后16进制数0x4d就会变为0X4D。
1 | int main() |
fixed
当 floatfield 设置为 fixed 时,浮点值将使用定点表示法写入:该值的小数部分位数与精度字段( precision ) 指定的位数完全相同,并且没有指数部分。
默认浮点表示法、定点表示法、科学计数法
默认浮点表示法和定点表示法以及科学计数法之间有所不同(请参阅 precision )。在默认浮点表示法中,精度字段指定小数点前后显示的是最大有意义位数,而在定点表示法和科学计数法中,精度字段精确指定小数点后显示多少位数字,即使这些数字是小数点后的零。
1 | // modify floatfield |
output:
1 | default: |
基于流析出的形式
>>称作流析出运算符(extraction operator)。
istream中的pf
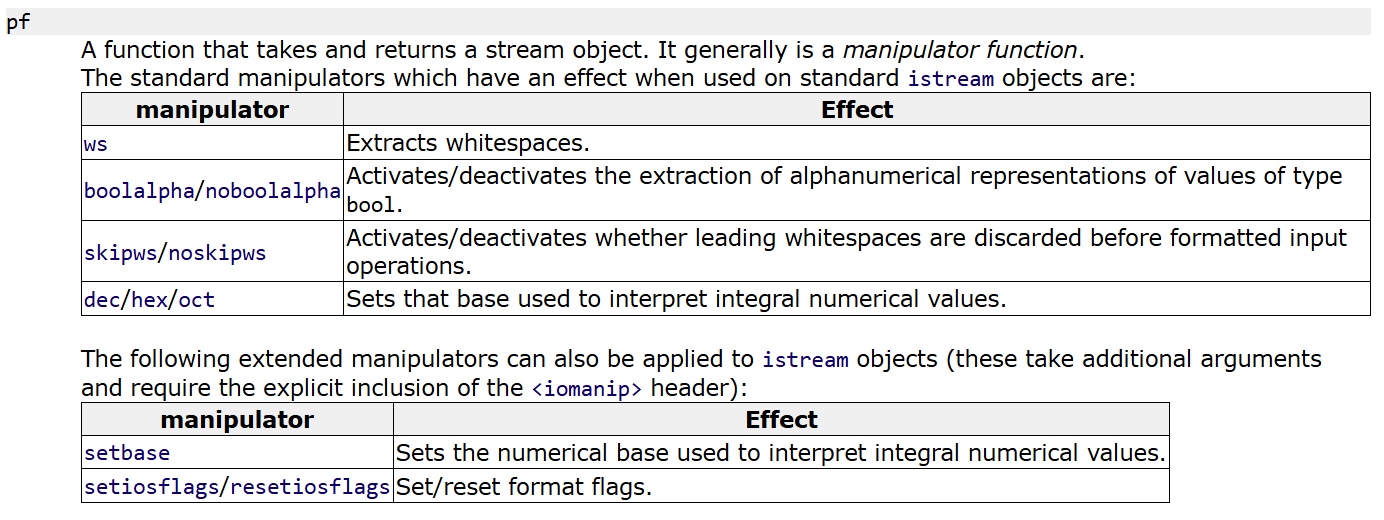
可以看到,相比于ostream的pf,istream中的可选项少了一些。
- boolalpha,可以通过输入false、true字符串从而给bool变量写值的操作。
dec/hex/oct,可以通过输入十进制、十六进制、八进制数字进而给整型变量写值。