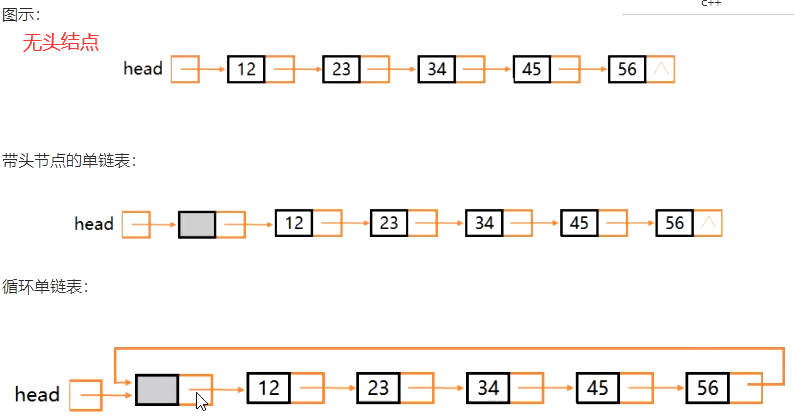
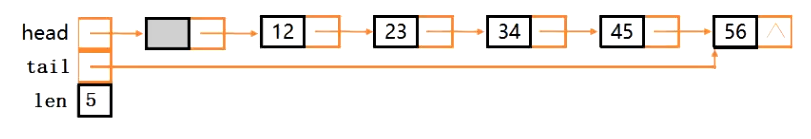
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
| #include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"sqlist.h"
#include<string.h>
void Init_sqlist(PSqlist plist)
{
assert(plist!=NULL);
memset(plist->arr,0,sizeof(arr));
plist->length = 0;
}
bool Insert_Pos(PSqlist plist, int pos, int val)
{
assert(plist!=NULL);
if( pos<0 || pos > plist->length || IsFull(plist) )return false;
for(int i = plist->length-1; i>=pos ;i--)
{
plist->arr[i+1] = plist->arr[i];
}
plist->arr[pos] = val;
plist->length++;
return true;
}
bool Push_Front(PSqlist plist, int val)
{
assert(plist!=NULL);
return Insert_Pos(plist, 0, val);
}
bool Push_Back(PSqlist plist, int val)
{
assert(plist!=NULL);
return Insert_Pos(plist, plist->length, val);
}
bool Del_val(PSqlist plist, int val)
{
assert(plist!=NULL);
return Del_pos(plist, FindPos_withVal(plist, val) );
}
bool Del_pos(PSqlist plist, int pos)
{
assert(plist!=NULL);
if( pos<0 || pos > plist->length || IsEmpty(plist) )return false;
plist->length--;
for(int i = pos; i < plist->length-1 ;++i)
{
plist->arr[i] = plist->arr[i+1];
}
return true;
}
bool Pop_Front(PSqlist plist)
{
assert(plist!=NULL);
Del_pos(plist, 0);
}
bool Pop_Back(PSqlist plist)
{
assert(plist!=NULL);
Del_pos(plist, plist->length);
}
int FindPos_withVal(PSqlist plist, int val)
{
assert(plist!=NULL);
int pos = -1;
int i = 0;
while(i< plist->length && val!=plist->arr[i])
{
++i;
}
if(i!=length)
{
pos = i;
}
return pos;
}
bool IsEmpty(PSqlist plist)
{
return plist->length == 0;
}
bool IsFull(PSqlist plist)
{
return plist->length == sizeof(plist->arr)/sizeof(plist->arr[0]);
}
void Clear(PSqlist plist)
{
assert(plist!=NULL);
plist->length = 0;
}
void Destory(PSplist plist)
{
assert(plist!=NULL);
Clear(plist);
}
|