内容
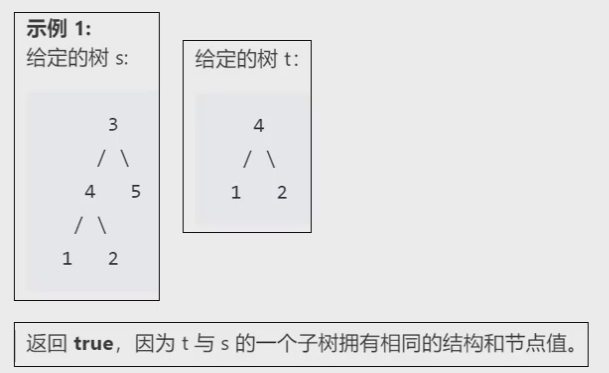
原题名叫做:另一个树的子树。总的来说就是找一个树T1中有没有和T2完全结构一样的子树。
分析
要判断树中是否包含某个具体的结构,可以使用遍历序列来判断。
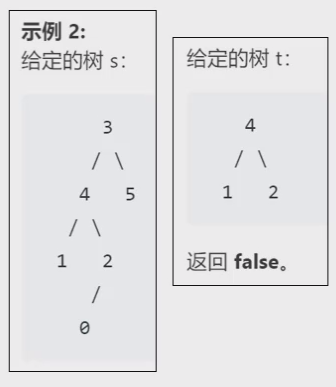
但是要注意:示例2就是一种容易忽略的情况。如果仅仅依靠非空节点的遍历序列去判断,则就会忽略掉T1中的比T2多余的部分,比如:T1的前序遍历为341205,T2的前序遍历为412。虽然T1包含T2的序列412,但是T1的2节点下面还挂着左孩子0。这就导致实际上T1中这个子树和T2结构不完全一样!
所以,还要给叶子节点的空孩子加标记符,比如#代表空。
如此,T1的前序遍历为341##20#5##,T2的前序遍历为41##2##,这样就能区分了。
除此之外:还要在每次写val值(包括空)之后附加个!标记,因为122334有可能是12,23,34,也有可能是1,223,34。这就造成了歧义。
补充一句,前序、中序、后序选择哪一个都可以,只要给出有效节点值、空节点以及访问节点结束标志,就能完全确定一个树的结构。
代码
解1_两树序列化为字符串,判断是否包含子串
Java中字符串不断的拼接一定要用StringBuilder。可以提高效率。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| package 字符串;
import common.TreeNode;
public class _572_另一个树的子树 {
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
}
private String postSerialize(TreeNode root)
{
StringBuilder sb = postSerialize(root, sb);
return sb.toString();
}
private void postSerialize(TreeNode root, StringBuilder sb)
{
if(root != null)
{
postSerialize(root.left, sb);
postSerialize(root.right, sb);
sb.append(root.val);
}
else
{
sb.append("#");
}
sb.append("!");
return;
}
}
|
测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| import common.TreeNode;
import common.printer.BinaryTreeInfo;
import common.printer.BinaryTrees;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(3);
root.right = new TreeNode(5);
root.left = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode curRoot = root.left;
curRoot.left = new TreeNode(1);
curRoot.right = new TreeNode(2);
BinaryTrees.println(new BinaryTreeInfo() {
@Override
public Object root() {
return root;
}
@Override
public Object left(Object node) {
return ((TreeNode)node).left;
}
@Override
public Object right(Object node) {
return ((TreeNode)node).right;
}
public Object string(Object node) {
return ((TreeNode)node).val;
}
});
System.out.println(postSerialize(root));
}
|
结果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| ┌─3─┐
│ │
┌─4─┐ 5
│ │
1 2
#!#!1!#!#!2!4!#!#!5!3!
|
isSubtree函数:对比两个字符串,判断T1字符串是否包含T2字符串。可以调用java的库函数contains。但据说contains用的不是KMP,因此效率可能较低,最好调用KMP算法。
1
2
3
4
| public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
if(root == null || subRoot == null) return false;
return postSerialize(root).contains(postSerialize(subRoot));
}
|
坑
虽然前序、中序、后序都可以,但是以上先序遍历转化的字符串有缺陷,仍不能通过T1先序字符串包含T2先序字符串就断定T2一定是T1的子树。比如:T1是33单节点,那么T1的字符串为33!#!#!,T2为3单节点,那么T2的字符串为3!#!#!,可以看到,虽然T1字符串包含T2字符串,但是T2的3节点压根就跟T1的33节点没关系!
于是,可以看到,前序遍历是存在缺陷的,这个缺陷只出现在顶点打印的歧义。
中序、后序都没有这样的问题。所以,如果是用前序遍历来序列化树,那么要在打印的最开始再另加一个标志如?,如此:T1字符串变为?33!#!#!,T2字符串变为?3!#!#!,由此就可以判别出,T1字符串不包含T2字符串了,因此可以正确判断出,T2不是T1的子树。
心得
这个题目属于二叉树的结构方面的问题,类似这类题型,考虑利用二叉树序列的特点和意义,转化为字符串序列,相当于把不好解决的树形结构降维打击成了一维结构。所以,本质上,这个题目考察的是二叉树的序列化、反序列化。
总结
- 非空节点:
值!,空节点:#!
- 空节点也必须序列化,才能完整地表达唯一的一棵树,而且前序、中序、后序遍历都可以确定一棵树,但是层序遍历不可以。

