参考文章:一文讲透 Git 底层数据结构和原理 - 阿里开发者的文章 - 知乎 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/142289703
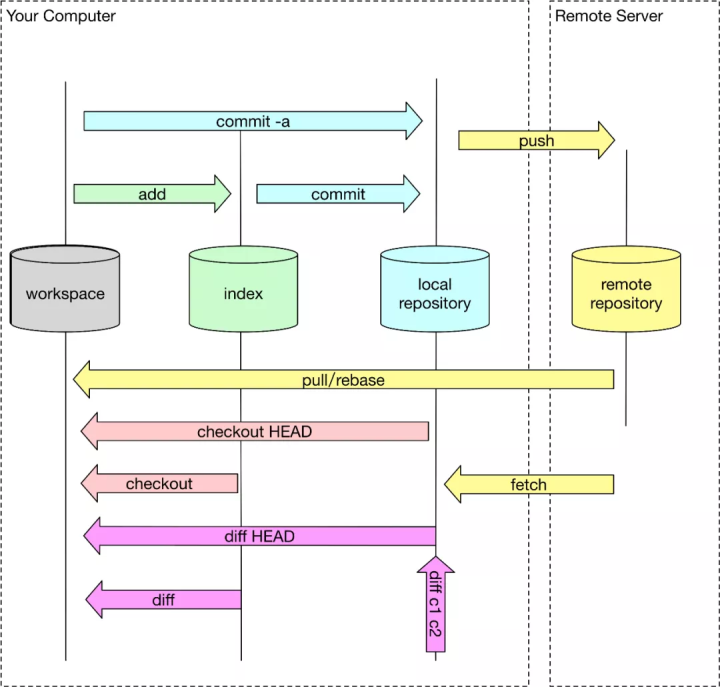
简要说明
| 命令 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| checkout | Switch branches or restore working tree files |
| reset | Reset current HEAD to the specified state |
| revert | Revert some existing commits |
| rebase | Reapply commits on top of another base tip |
| switch | Switch branches |
| restore | Restore working tree files |
可以看出,checkout实际上是switch和restore的结合。
对应的场景
checkout
两个作用,一是切换分支,二是恢复工作区代码。如果checkout相同分支,则作用就是恢复工作区代码。因此,可以作用于,想要把未add的代码恢复到最新commit的状态。
reset
git reset --mixed:此为默认方式,等同于不带任何参数的git reset。这种方式,只保留源码,回退commit和index信息git reset --soft:回退到某个版本,只回退了commit的信息,如果还要提交,直接commit即可(修改的内容变成未add的状态),索引(暂存区)和工作目录的内容是不变的,在三个命令中对现有版本库状态改动最小。git reset --hard:彻底回退到某个版本,本地的源码也会变为上一个版本的内容,所有修改的内容都会丢失, (修改的代码 不会变成未add的状态)。索引(暂存区)内容和工作目录内容都会变给定提交时的状态。
revert
revert我们commit了三个版本(版本一、版本二、 版本三),突然发现版本二不行(如:有bug),想要撤销版本二,但又不想影响撤销版本三的提交就可以用 git revert 命令来反做版本二,生成新的版本四,这个版本四里会保留版本三的东西,但撤销了版本二的东西
参考链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/ef34fa4c8bf8
rebase
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42310154/article/details/119004977
git回退
只回退单个文件
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/267141048
Git在2.17中新增两个命令,restore和switch,分担checkout的职责;
1 | # 放弃工作区的内容,使保持与暂存区一致 |
这里的默认参数是
--worktree(工作区)
暂存区单个文件放弃修改:
1 | # 放弃暂存区的内容,使与最近一次提交保持一致(HEAD) |
这里是暂存区的内容发生了变化,工作区的内容不会受影响
工作区单个文件恢复到某个提交版本
1 | # 恢复工作区的某个文件到指定的某个版本,如果文件有修改也会被覆盖 |
恢复操作执行后需要add
暂存区单个文件恢复到某个提交版本
1 | # 恢复暂存区的某个文件到指定的某个版本,如果暂存区文件有未提交也会被覆盖 |
如果需要将工作区与暂存区的某个文件都恢复到之前某个提交版本,则使用checkout来操作,简称co
1 | # 同时将工作区与暂存区的某个文件恢复到指定版本 |